
At Lyell, It’s All About the Cells
We are designing CAR T cells with potent and durable antitumor cytotoxicity.
-
We first identify promising targets
We look for targets that are highly expressed on tumor cells to enhance benefit, and have low expression or are inaccessible in normal tissue to avoid on-target, off-tumor toxicity.
-
We then arm CAR T-cells with enhancements designed to improve the T cell’s ability to fight cancer
We engineer a patient’s own living immune cells and arm them with one or more of our innovative enhancements. These include CAR constructs, technologies, and manufacturing protocols designed to give T cells more potent cancer cell killing capabilities. These enhancements are designed to improve CAR T-cell expansion, tumor infiltration, cytotoxicity, and persistence.
-
Our goal is to develop one-time CAR T-cell therapies
Our therapies are designed to deliver lasting remission for patients with cancer. We have two product candidates in clinical development, as well as earlier stage product candidates in preclinical development.
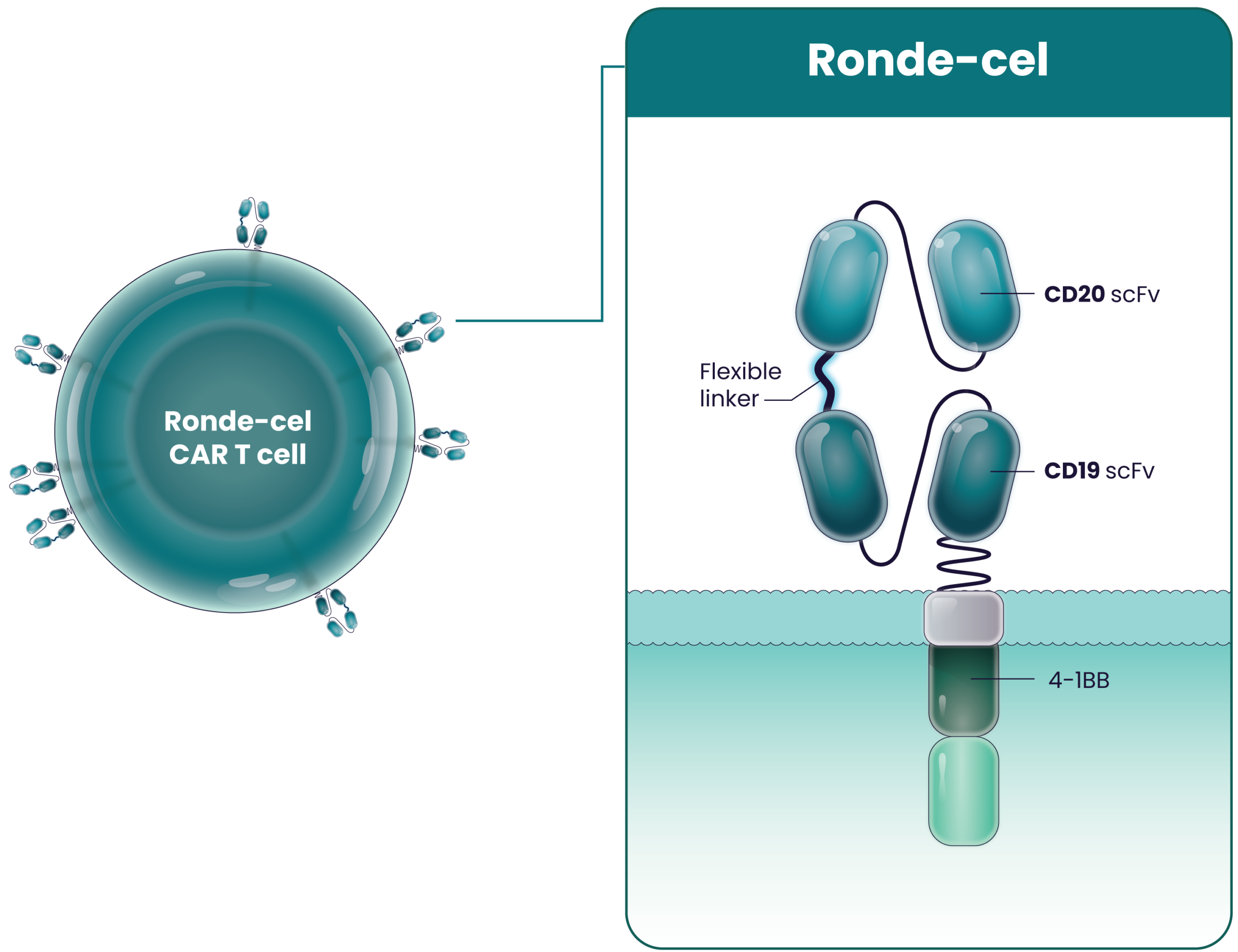
Ronde-Cel
Ronde-cel is our next-generation CAR T-cell product candidate in development for the treatment of patients with aggressive large B-cell lymphomas. It is an autologous dual-targeting CD19/CD20 CAR T-cell therapy designed to recognize and kill two targets – CD19 and/or CD20 antigens expressed on B cells. Ronde-cel is rationally designed with a true CD19/CD20 “OR” logic-gated CAR targeting either CD19 or CD20 with full potency. This differentiates ronde-cel from cell therapies and other therapeutic modalities that singularly target CD19, CD20, or CD22. Additionally, ronde-cel is manufactured to produce a CAR T-cell product with higher proportions of naive and central memory T cells through a process that enriches for CD62L-expressing cells. Importantly, the enrichment of CD62L-expressing T cells does not increase the manufacturing time. We can deliver ronde-cel to patients on a timeline similar to those of the currently approved CD19 CAR T-cell therapies.

Ronde-Cel’s Proposed Mechanism of Action
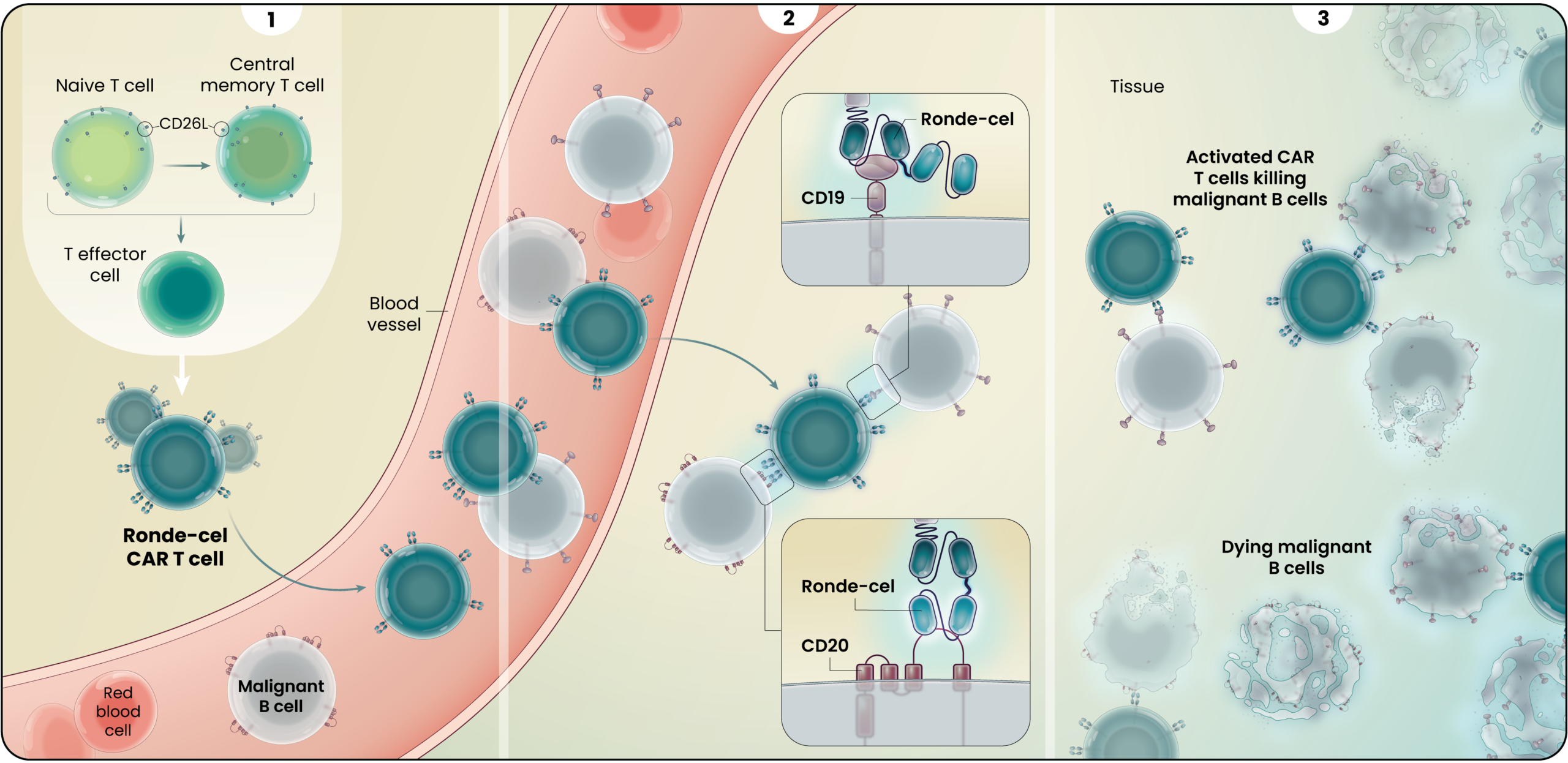

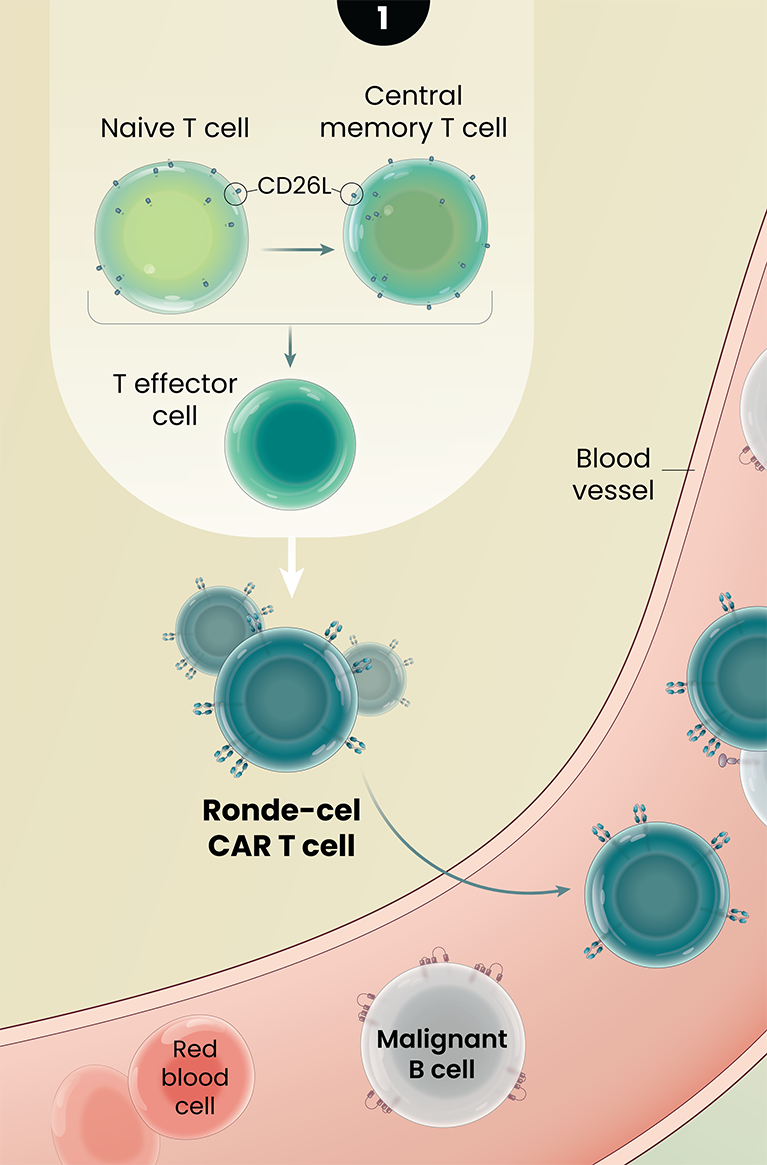
1
Ronde-cel is manufactured to enrich for naive and central memory cells via selection for CD62L-positive cells. These less differentiated cells have been associated with improved persistence, reduced exhaustion, and lower adverse cytokine production compared to CAR T cells generated from traditional processes.1
2
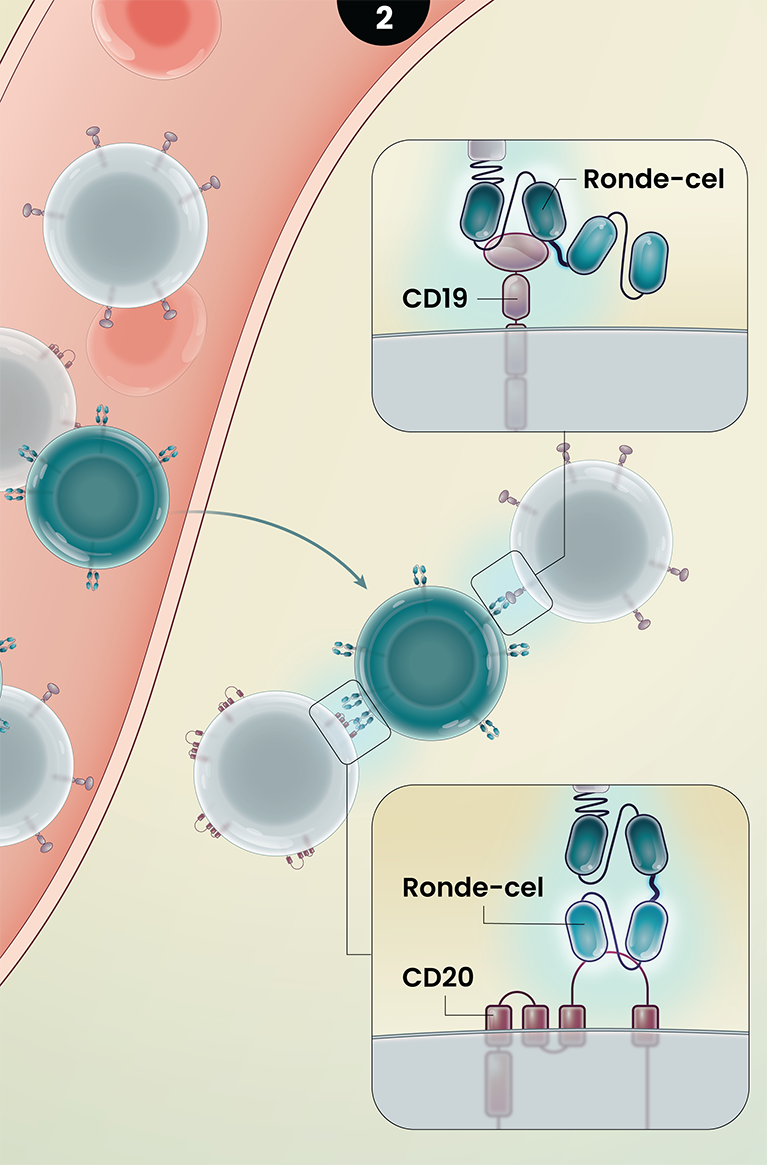
Ronde-cel is an autologous dual-targeting CD19/CD20 CAR T-cell product candidate designed to recognize two targets, CD19 and/or CD20 antigens expressed on malignant lymphoma cells. These dual-targeting CAR T cells are designed to help more patients achieve complete remission by killing lymphoma cancer cells that express either one or both targets.
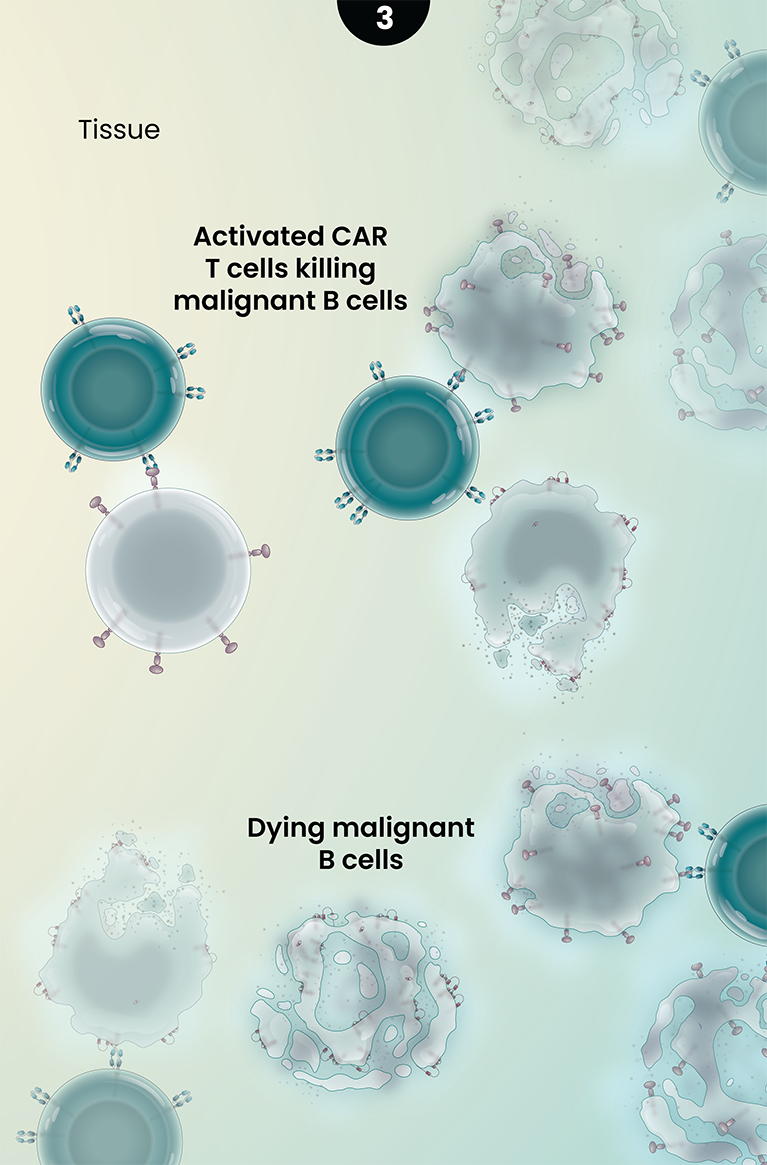
3
Together, the novel dual-targeting CAR construct and the enrichment for naive and central memory T cells are designed to provide multiple benefits over currently approved CD19 CAR T-cell therapies as they circulate and target malignant B-cells throughout the body. These potential benefits may include:
- Ability to target lower or heterogeneous CD19 antigen density and result in a higher percentage of complete responses;
- Increase in the duration of responses by preventing relapse due to CD19 antigen escape; and
- Longer duration of responses driven by better cell expansion, persistence, and reduced exhaustion.
LYL273
LYL273 is a guanylyl cyclase-C (GCC) targeted CAR T-cell product candidate for the treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) and other GCC-expressing cancers. GCC is a target expressed on 95% of colorectal cancers and a majority of pancreatic adenocarcinomas.
LYL273 is designed to overcome two efficacy barriers in solid tumors: insufficient in vivo expansion post infusion and the hostile or “immunologically cold” tumor microenvironment that employs multiple mechanisms to suppress T-cell infiltration, activation and tumor killing.
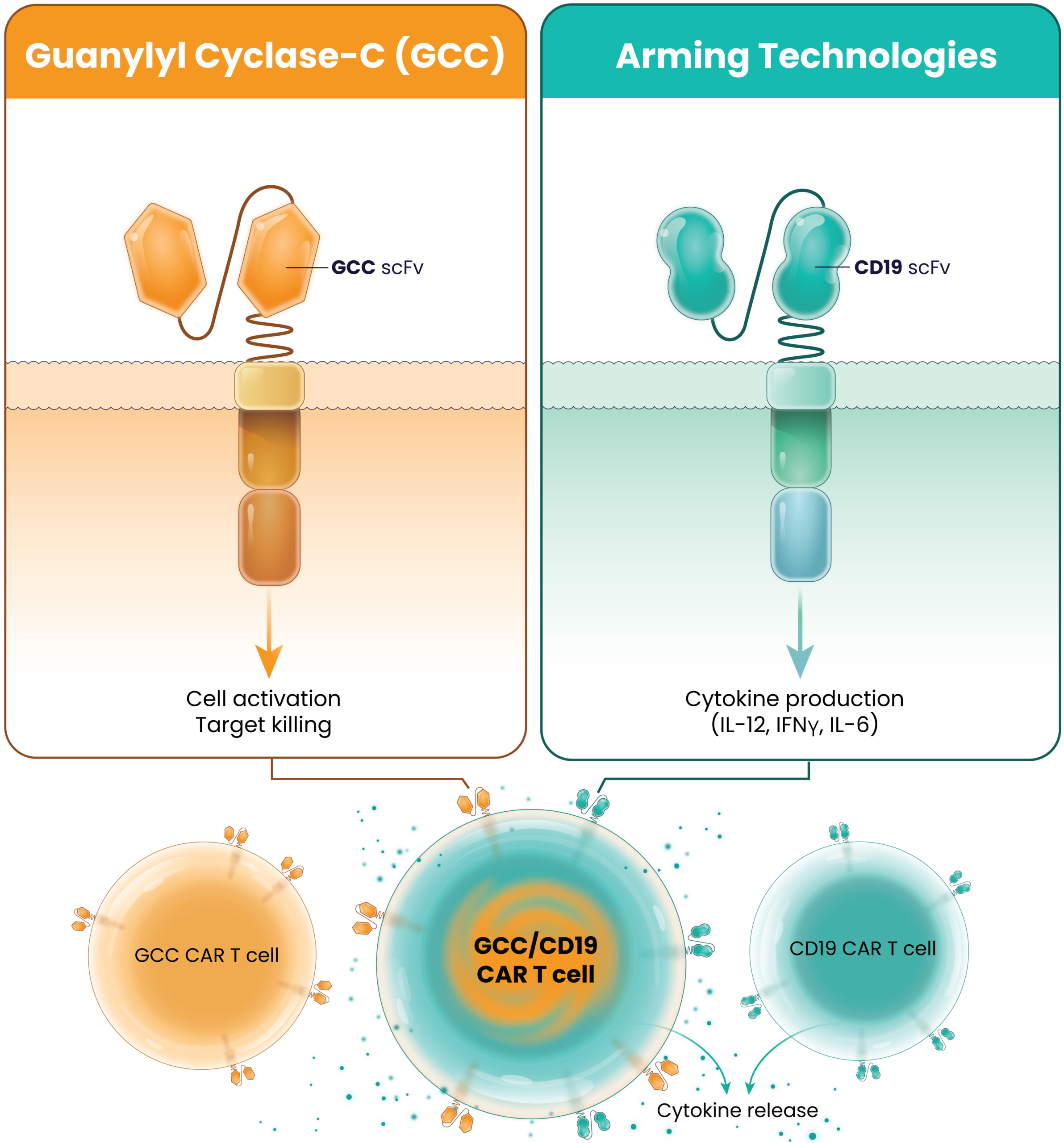
The robust 7-day manufacturing process produces consistent LYL273 CAR T-cell products with 3 key CAR T-cell types:
GCC CAR T cells, CD19 CAR T cells, and GCC/CD19 “doublet” CAR T cells.

LYL273’s Proposed Mechanism of Action
Guanylyl cyclase-C, or GCC, expression is limited to the apical surface or the luminal side of the colon, making it less accessible to CAR T cells. In colorectal cancers, this polarity in GCC expression is disrupted, exposing the GCC antigen to CAR T cells, that can then target and kill the cancer cells while sparing the adjacent healthy gastrointestinal tissue as illustrated below.
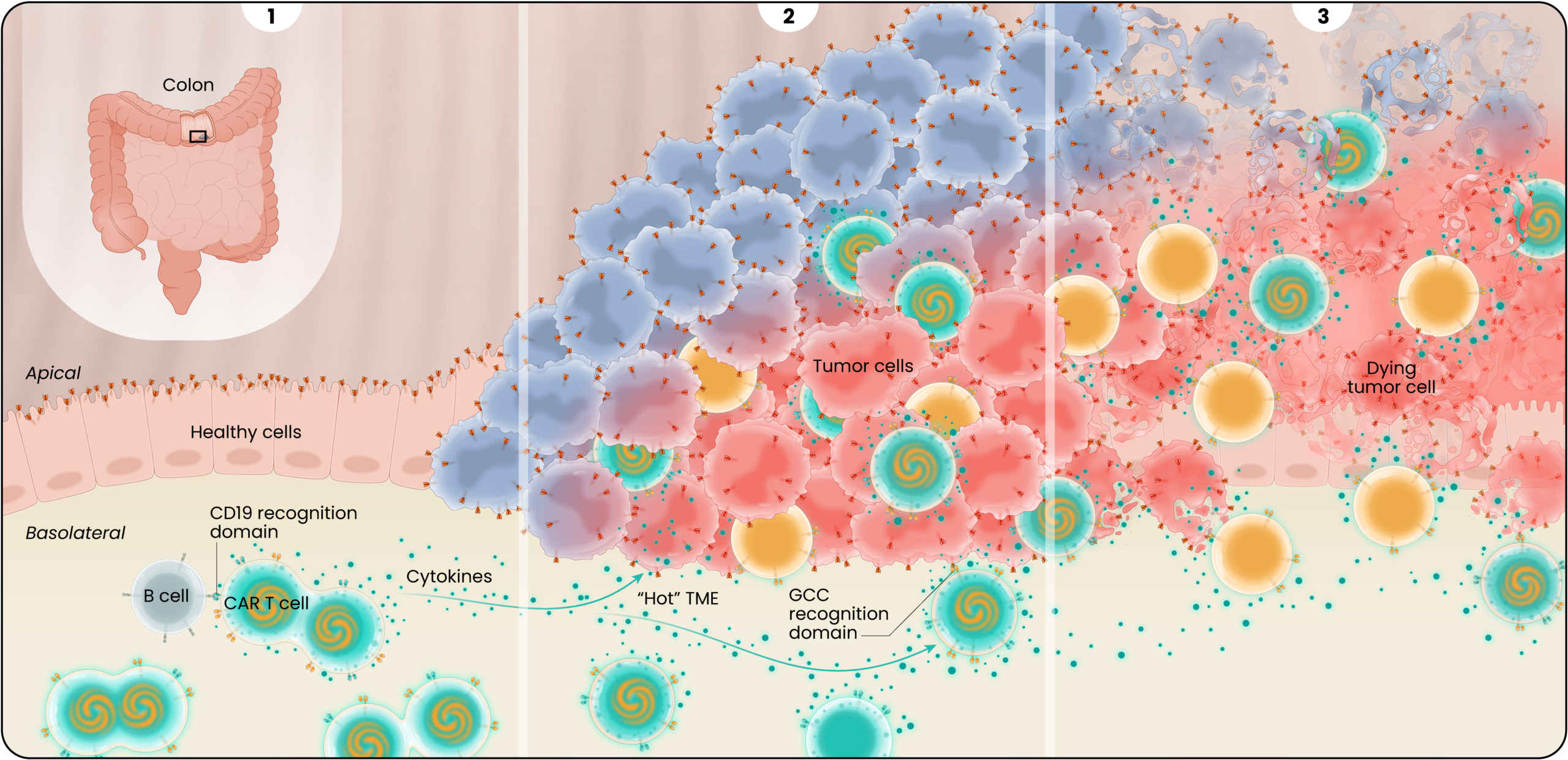

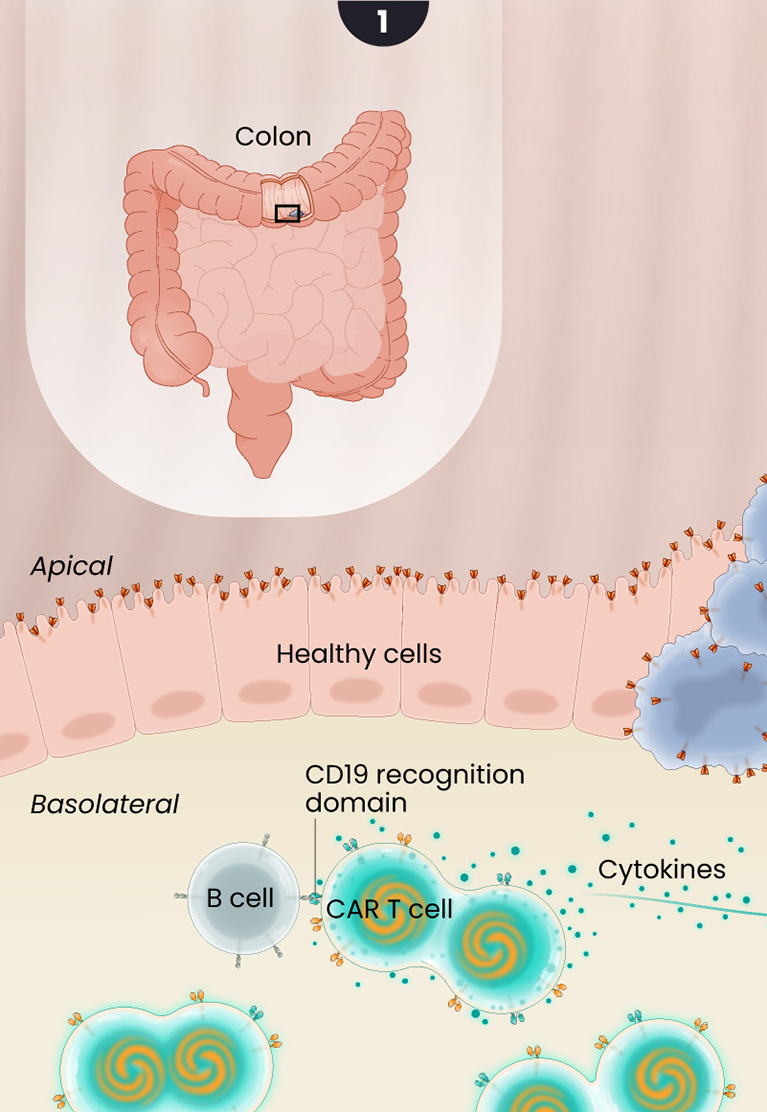
1
After LYL273 CAR T cells are infused, they rapidly encounter B cells in the circulation. Upon binding to the B cells, cytokines are released and the GCC/CD19 “doublet” CAR T cells begin to expand and multiply. These cells become available to attack the cancer cells but avoid targeting healthy cells in the polarized gut epithelium where GCC antigen is sequestered from the circulation.
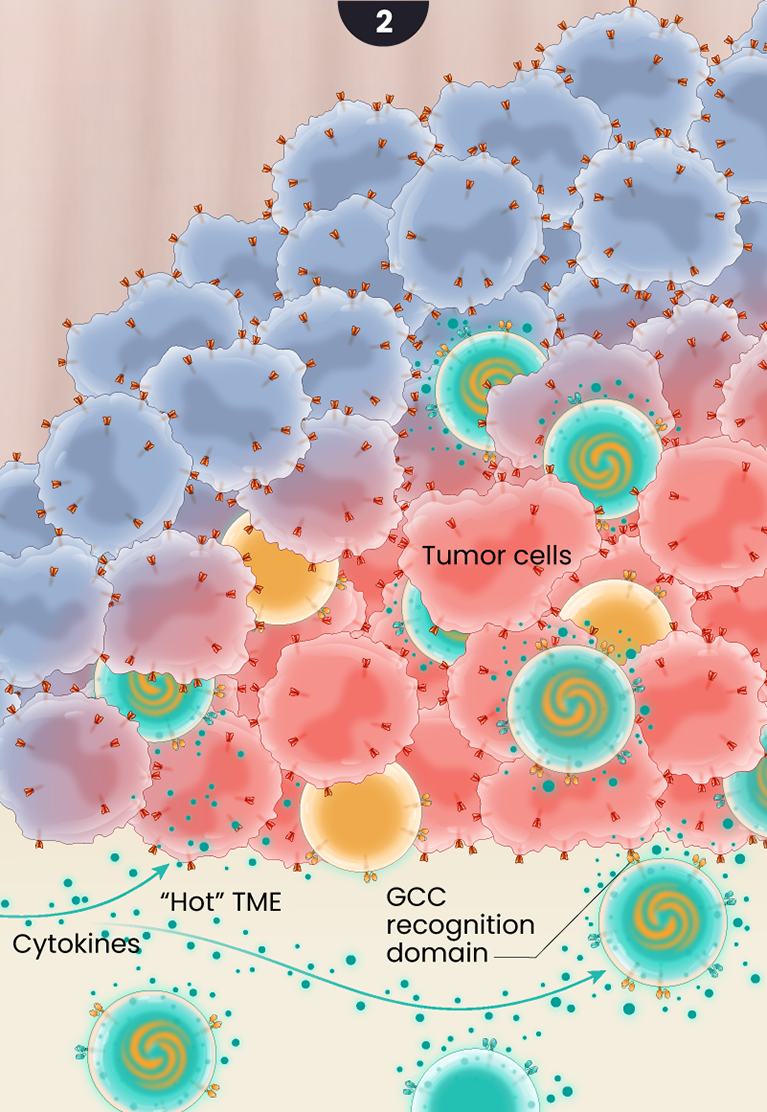
2
The GCC/CD19 doublet and the GCC CAR T -cells infiltrate the tumor where they bind to and kill colorectal cancer cells and the doublet cells release cytokines in a controlled fashion creating antitumor or pro-inflammatory signaling. The cytokine secretion is believed to “warm up” the hostile or “immunologically cold” tumor microenvironment, helping to recruit additional cancer-killing immune cells to help support the GCC-targeted CAR T cells.
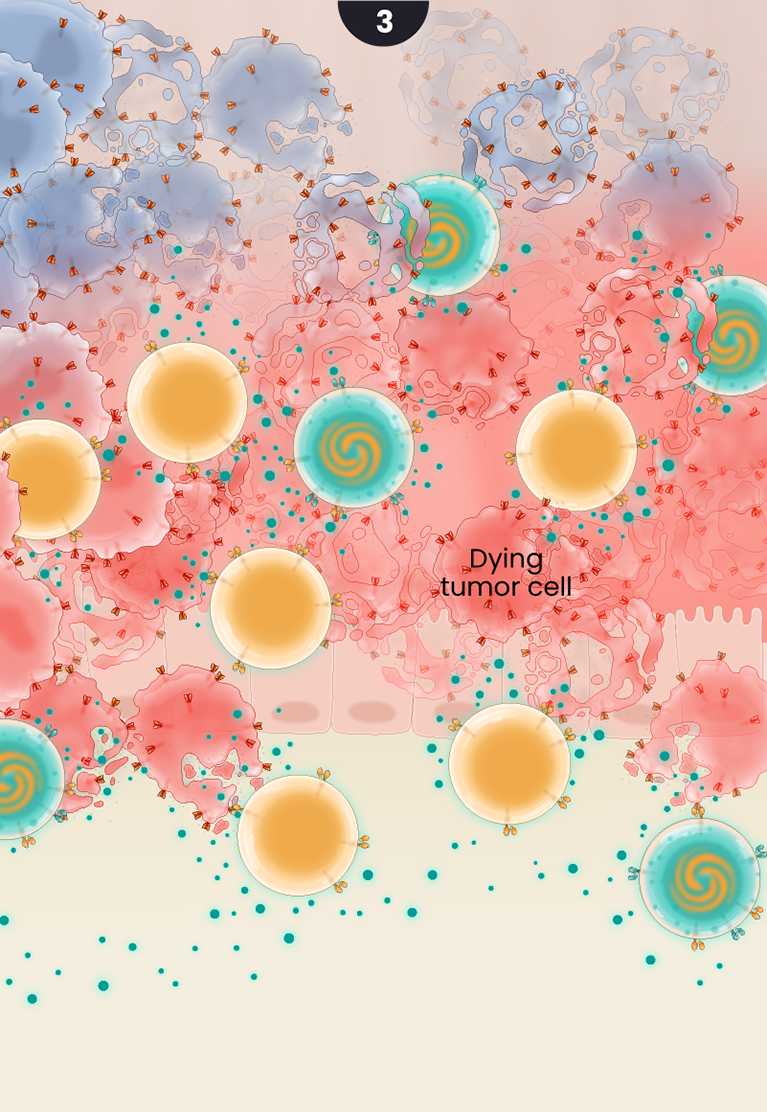
3
Partnering the GCC CARs with the cytokine-secreting CD19 CARs results in effective cancer cell killing by ensuring adequate cell expansion, tumor infiltration, and recruitment of additional supporting immune cells.